The core of the diode is the PN junction. Therefore, the unidirectional conductivity of the diode is determined by the characteristics of the PN junction. Near the interface between the P-type and N-type semiconductors, because the free electron concentration in the N region is large, the negatively charged free electrons will diffuse from the N region to the P region with a low electron concentration. The result of the diffusion makes the PN junction rely on P One side of the zone is negatively charged, and the side close to the N zone is positively charged, forming an electric field from the N zone to the P zone. That is, the electric field in the PN junction. The internal electric field will hinder the continued diffusion of majority carriers, which is also called a barrier layer.
(1) PN junction plus forward voltage. Connect the P area of ​​the PN junction to the positive pole of the power supply and the N area to the negative pole of the power supply. At this time, the electric field generated by the applied voltage on the PN junction is opposite to the direction of the electric field in the PN junction, which weakens the PN. The electric field in the junction allows the majority of carriers to smoothly pass through the PN junction to form a forward current, which increases rapidly with the increase of the applied voltage, that is, the PN junction is in a conducting state when the forward voltage is applied.
(2) In the case of PN junction plus reverse voltage, connect the P area of ​​the PN junction to the negative pole of the power supply, and the N area to the positive pole of the power supply. At this time, the electric field generated by the applied voltage on the PN junction is in the same direction as the electric field in the PN junction, which strengthens the PN junction In the internal electric field, it is difficult for most carriers to pass through the PN junction under the action of the electric field force. The reverse current is very small, that is, the PN junction is in an off state when the reverse voltage is applied.
Unidirectional conductivity of the diode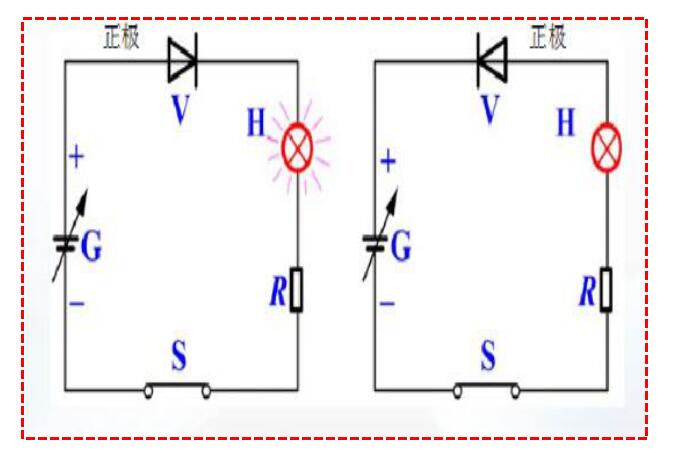
(1) Positive electrode potential> negative electrode potential, the diode is turned on;
(2) The positive pole potential <the negative pole potential, the diode is cut off.
That is, the diode is forward-biased on and reverse-biased off. This conductivity characteristic is called the unidirectional conductivity of the diode.
Diode has unidirectional conductivity(1) The diode is turned on when the forward voltage is applied
Connecting the anode of the diode to the high potential in the circuit and the cathode to the low potential is called forward bias (forward bias). At this time, the inside of the diode presents a smaller resistance and a larger current flows. This state of the diode is called the forward conduction state.
(2) Reverse voltage diode cuts off
Connecting the anode of the diode to the low potential in the circuit and the cathode to the high potential is called reverse bias (reverse bias). At this time, the inside of the diode presents a large resistance and almost no current flows. This state of the diode is called the reverse cut-off state.
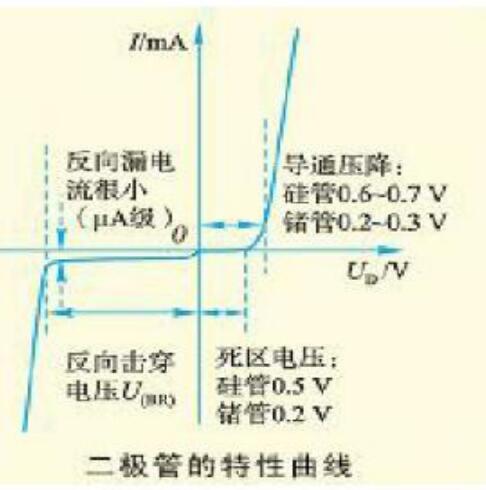
Characteristic curve of diode1. Positive characteristics
When the forward voltage is small, the diode presents a large resistance and is basically in the off state. This area is often called the "dead zone" of the forward characteristic. Generally, the "dead zone" voltage of a silicon diode is about 0.5 volts, and a germanium diode Approximately 0.2 volts.
When the forward voltage exceeds the "dead zone" voltage, the resistance of the diode becomes very small and the diode is in a conducting state. After the diode is turned on, the voltage drop at both ends remains basically unchanged. The silicon diode is approximately 0.7 volts, and the germanium diode is approximately 0.3 volts. as the picture shows.
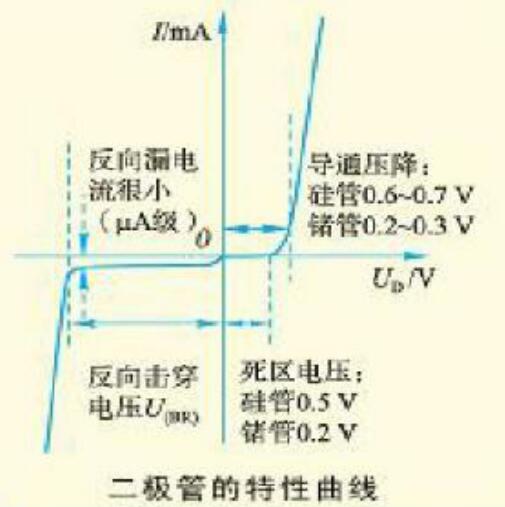
2. Reverse characteristics
(1) When reverse voltage is applied to the diode in the reverse cut-off area, there will still be a reverse current flowing through the diode, which is called leakage current. The leakage current basically does not change with the change of the reverse voltage, which is called the reverse cut-off area.
(2) Reverse breakdown area When the reverse voltage applied to both ends of the diode exceeds a certain value, the reverse current suddenly increases. This phenomenon is called reverse breakdown. In practical applications, ordinary diodes should avoid working in the breakdown range. as the picture shows.
APM ac DC Power Supply is built-in standard automobile electrical testing curves,users can select any built-in curve to do the DUT performance test directly according to their demand. High voltage dc power supply meets different application demands.
Some features of the Variable voltage dc power supply as below:
- Ultrafast respond time and high efficiency
- Accurate voltage and current measurement capability
- Constant Power and wide range of voltage and current output
- Equips with LIST waveform editing function
- Compliant with SCPI communication protocol
- Support RS232/RS485/LAN/USB (standard) ,GPIB (optional)
- Master/Slave parallel and series operation mode for up to 10 units
- Built-in standard automobile electrical testing curves
- Full protection: OVP/OCP/OPP/OTP/SCP
- Voltage drop compensation by remote sense line.
- Have obtained CE,UL,CSA,FCC.ROHS
600V DC Power Supply,Programmable Power Supply,Switch Mode Power Supply,9 Volt DC Power Supply
APM Technologies Ltd , https://www.apmpowersupply.com