At the moment you arrive at the office this morning, you may have used 4 radio frequency tags (RFID) without knowing it: when you insert the car key and turn off the anti-theft lock system circuit; When you drive through an unpaid toll booth to pay for it automatically; when you use your mobile phone to pay for morning coffee, when you use your ID to register into the office. RFID may not be widely available, but it is gradually becoming successful.
The first passive transponders powered by RF inputs date back to the early 1970s, as were the case with most of today's RFID applications. It is the gratifying progress of today's semiconductor technology that makes RFID really take off.
In the commercial market, RFID offers unprecedented opportunities to increase productivity and improve the user experience by providing very granular data and automating services such as payment and record retention. RFID is widely used in a variety of applications, such as livestock identification, retail inventory management, medical record management, electronic non-stop charging, e-passports, and more recently, which will be an important driver of specific RFID technologies.
The market for RFID tags (identity part of RFID) is growing rapidly and is expected to accelerate. For example, IDTechEx predicts that the number of passive RFID tags will increase from less than 3 billion in 2011 to about 250 billion in 2021.
From an engineering perspective, RFID is not a single technology, it varies with frequency. It can use a variety of carrier frequencies, but three of them dominate (see Table 1). The low frequency (LF) uses the 125kHz to 135kHz band and the high frequency (HF) operates at 13.56MHz. UHF (Ultra High Frequency) is mainly used in the 865MHz to 955MHz band, although it may also include the 2.4GHz band.
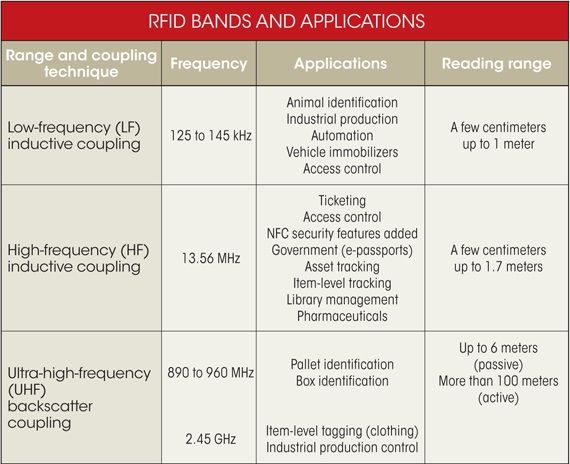
Table 1: RFID Bands and Applications
Most RFID system design work is focused on the reader system. The application and characteristics of transponders (labels) designed and manufactured by semiconductor companies will primarily determine the design of the reader. In general, there are two types of tags that can be used to communicate with readers: active tags with embedded batteries, and passive tags without batteries. Passive tags are more common, and this article will only discuss passive tags.
Perkins 76-200KW Diesel Generator
Perkins 76-200Kw Diesel Generator,Perkins Silent Type Diesel Generator,Perkins Container Type Diesel Generator,Perkins Super Silent Diesel Generator
Shanghai Kosta Electric Co., Ltd. , https://www.generatorksd.com