With the draft of the sub-6GHz part of the NR part of the 3GPP first edition in December 2017, and the subsequent draft of Phase 2, the semiconductor manufacturers and terminal manufacturers began to commercialize based on the relevant drafts. In the process of rapid commercialization, there will inevitably be many problems in software and testing. How to analyze the current situation and realize fast customs clearance in software and testing has become one of the hot issues of 5G development. Let's take a look at the relevant content.
At the 7th EEVIA China ICT Media Forum and 2018 Industry and Technology Outlook Seminar, NI China Technology Market Engineer Mr. Ma Lisi analyzed and shared related issues.

5G now has three application scenarios, namely, enhanced mobile networks with high bandwidth and data throughput requirements, low-power application networks for Internet of Things (IoT), and ultra-low latency applications for scenarios such as driverlessness. The internet.
For the 5G landing time, 3GPP and ITU have also made corresponding plans, as shown in Figure 1.
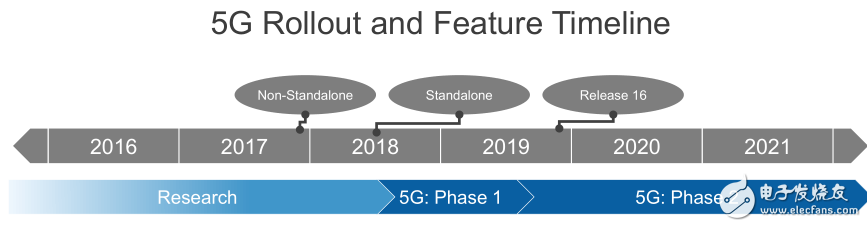
Figure 1 3GPP and ITU planning for 5G landing time
From the 5G NR part, it can be divided into Phase 1 and Phase 2, and with the 3GPP first version of sub-6GHz landing in December 2017 (belonging to Release 15 version), the physical layer of Phase 1 and some parameters. The specifications at the level are also relatively clear.
New requirements for 5G new features for test equipment Subcarrier spacingAn important change in the new version of the 5G New Radio Sub-6GHz portion relative to 4G LTE is the variation in subcarrier spacing. The 4G domestic uses a fixed subcarrier spacing of 15 kHz, but the 5G NR uses a flexible subcarrier spacing. This is mainly because the millimeter wave band will also be used as the 5G application band. When extending to the millimeter wave band, both the bandwidth and the subcarrier spacing need to be greatly adjusted. Such adjustments put forward new requirements for design and testing.
bandwidthIn terms of bandwidth, in addition to sub-6GHz, 400MHz bandwidth may be applied more in the millimeter wave section. For testers, especially for high-end RF front-end applications, it may also use digital pre-distortion, packets. The network tracking method requires higher bandwidth of the test equipment to meet the requirements of this design.
Independent networking and non-independent networkingNow that the 4G network has been widely deployed, and to upgrade to the 5G network, there is still a process of change in the middle of the networking form and deployment scenario. The version that landed in December 2017 proposed a non-independent networking (NSA). In this form of networking, the 4G LTE network and the 5G base station actually coexist, which means that the 5G mobile phone terminals in the past two years are still 4G to 5G. A switching process requires chips and production terminals designed by chip vendors and terminal manufacturers to support both 4G and 5G networks. In this way, the way to achieve 5G landing and commercialization more quickly, and then slowly transition to the independent networking (SA), that is, the access network and the core network are more in the form of 5G (specific Operators and terminal manufacturers refer to another manuscript for two network layouts :).
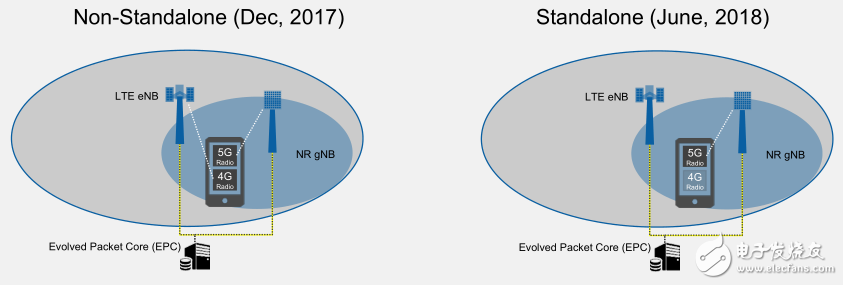
Figure 2 Independent networking and non-independent networking
The 5G network deployment form that has been clarified now poses many challenges for 5G testing. Especially for the non-independent networking form, 5G equipment is required to meet the 5G requirements while complying with the 4G requirements, thus causing interference, frequency bands, etc. The problem must be solved, and the relevant test equipment must also provide a complete test plan.
To sum up, the challenges faced by the current 5G test mainly include: The first is the improvement of complexity, including flexible parameter level, subcarrier spacing change, new requirements of RF front-end; the second is the coexistence of 4G and 5G, at the front end. The chip design is designed to be highly integrated into a single front-end chip; the third is the testing of more RF indicators, including high bandwidth, high modulation characteristics, and better EVM; the fourth is Test time and cost requirements, "fast" is a serious challenge in the 5G era.
5G new requirements for test instrumentsTraditional desktop instruments have many shortcomings. As shown in the left figure of Figure 3, engineers use many instruments every day, including spectrum analyzers, signal sources, network points, power supplies, source meters, etc. Many instruments not only take up a lot of space, but also are difficult to do. Synchronous measurements, especially for high-complexity automated tests, are particularly evident. NI integrates these platformed instruments, puts all instruments in a small chassis, and uses PXI technology to perform a good synchronization mechanism to help engineers complete the test.

Figure 3 Integrated and miniaturized test instruments
In terms of algorithms, NI deploys algorithms such as FFT and Fourier transform to FPGAs. Given the powerful processing power of FPGAs, it greatly improves the speed and efficiency of testing.
PXI-based 5G test platformFor the 5G NR part, NI recently launched a test platform (NI PXI "6 GHz 5G-NR solution" that meets the 3GPP Release 15 version. The platform is based on the PXI platform. Typical test indicators and support for the protocol are all available on the software. A brand new upgrade to meet 5G related protocol support and testing projects. And because it is a software-centric platform, it is relatively easy to upgrade and replace the protocol.
ZGAR FIT
ZGAR electronic cigarette uses high-tech R&D, food grade disposable pod device and high-quality raw material. All package designs are Original IP. Our designer team is from Hong Kong. We have very high requirements for product quality, flavors taste and packaging design. The E-liquid is imported, materials are food grade, and assembly plant is medical-grade dust-free workshops.
From production to packaging, the whole system of tracking, efficient and orderly process, achieving daily efficient output. We pay attention to the details of each process control. The first class dust-free production workshop has passed the GMP food and drug production standard certification, ensuring quality and safety. We choose the products with a traceability system, which can not only effectively track and trace all kinds of data, but also ensure good product quality.
We offer best price, high quality Vape Device, E-Cigarette Vape Pen, Disposable Device Vape,Vape Pen Atomizer, Electronic cigarette to all over the world.
Much Better Vaping Experience!

E-Cigarette Vape Pen,Disposable Device Vape,Vape Pen Atomizer,Latest Disposable E-Cigarette OEM vape pen,OEM electronic cigarette
ZGAR INTERNATIONAL(HK)CO., LIMITED , https://www.sze-cigarette.com